Xray chest, PA view mild increase in perihilar bronchial wall... Download Scientific Diagram

Diffuse bronchial wall thickening owing to infiltration with CLL, as seen in our patient, is rarely encountered. Pathologic studies have shown that leukemic cells in CLL have a propensity to infiltrate peribronchial tissue through lymphatic routes, which may be followed by permeation of bronchial walls . Similar infiltrations may occur in the.
Chest Xray. (a) Thickening of bronchial walls with no Download Scientific Diagram

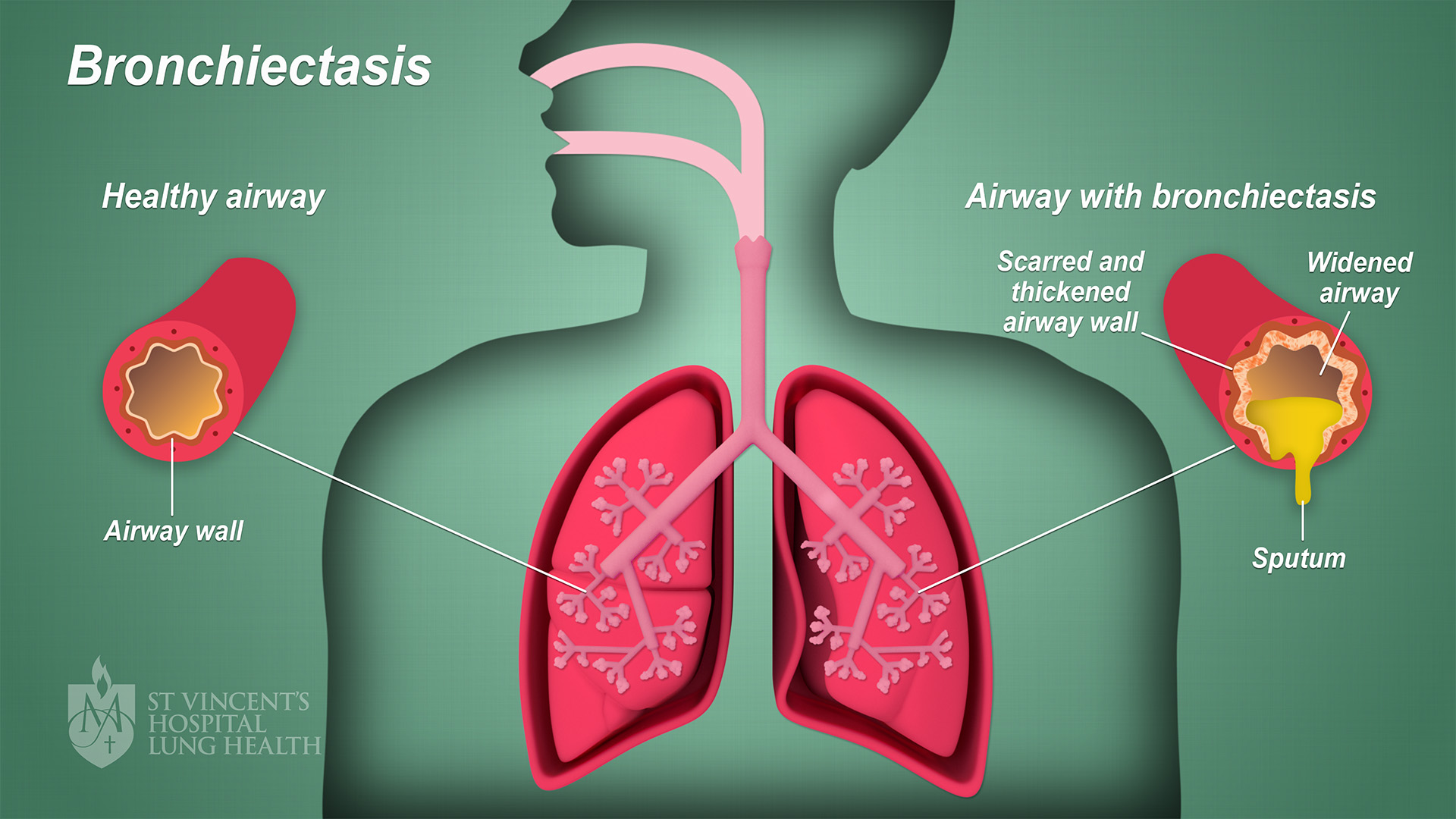
Bronchiectasis is when the walls of your bronchi, the tubes that carry air into and out of your lungs, become thickened and damaged. This makes it harder to breathe. You could have flare-ups of.
Bronchial wall thickness measurement in highresolution CT scan. Notes... Download Scientific

Bronchial wall thickening is the common final response of the airways to irritants, which cause the bronchi to become swollen and inflamed. Bronchiectasis/bronchial dilatation can develop in response to many aetiologies, including acquired conditions such as infection, pulmonary fibrosis, recurrent or chronic aspiration, as well as because of.
Bronchiectasis St Vincent's Lung Health
Identification of bronchial wall thickening is largely subjective. Because bronchiectasis and bronchial wall thickening often are multifocal rather than diffuse and uniform, a comparison of one lung region to another can be helpful in making this observation . It must be emphasized that using consistent window settings is very important in the.
Bronchus and branchial wall anatomy and diagram GetBodySmart
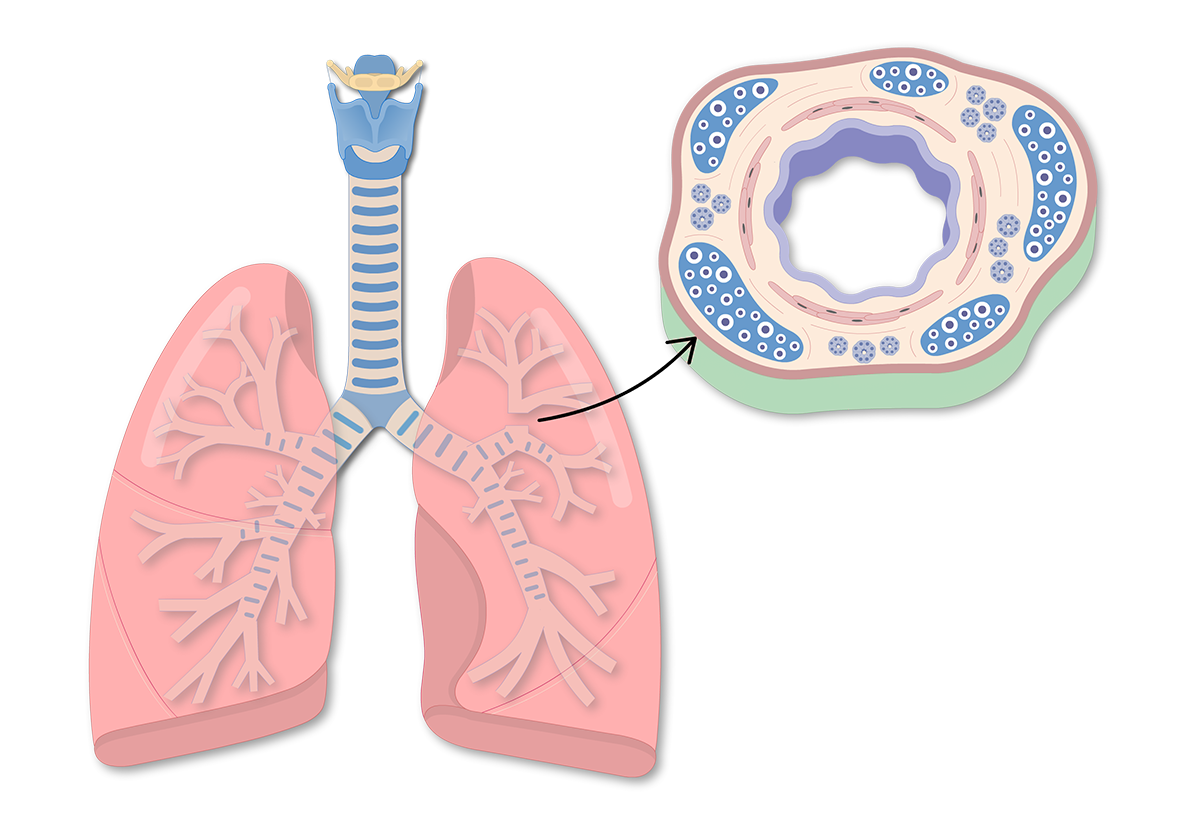
The bronchial walls of CRS subjects were significantly thicker than those of non-CRS subjects. CRS and asthma were related to bronchial wall thickening by multivariate linear regression analysis adjusted for age, smoking status, and chest symptoms. In addition, LMS was significantly correlated with bronchial wall thickening.
2a and 2bCT of thoraxlung window coronal section at the level of... Download Scientific Diagram

Bronchiectasis is a condition where damage causes the tubes in your lungs (airways) to widen or develop pouches. It makes it hard to clear mucus out of your lungs and can cause frequent infections. Coughing a lot with pus and mucus is the main symptom of bronchiectasis. Bronchiectasis can't be cured but can be managed with treatment.
Bronchioles function and diagram GetBodySmart
The commonest HRCT findings include bronchial dilatation, bronchial wall thickening, lack of normal bronchial tapering, any bronchi with an internal diameter greater than the diameter of the accompanying pulmonary artery (signet ring sign) and bronchi visible closer than two centimeters to the pleural surface (Table (Table2). 2).
A, CT image of peripheral bronchial wall thickening in a patient with... Download Scientific

Furthermore, reduction of bronchial wall thickening in the follow-up scan of smaller more peripheral airways after a therapeutic intervention can reduce visibility or make it disappear due to limitations in resolution. Sometimes airways with a normal diameter are misdiagnosed as bronchiectasis because of a thickened airway wall. Such thickening.
Thickening of the wall of the right main bronchus in IBD Eurorad

CT scan (1.5-mm collimation) obtained at level of left main bronchus depicts diffuse circumferential thickening of bronchial walls (arrows). Note high-attenuation regions in bronchial wall, likely representing calcification.. CT may also reveal mild intrathoracic tracheal wall thickening, frequently with ossification of the tracheal rings [2.
Chest Xray. (a) Thickening of bronchial walls with no Download Scientific Diagram

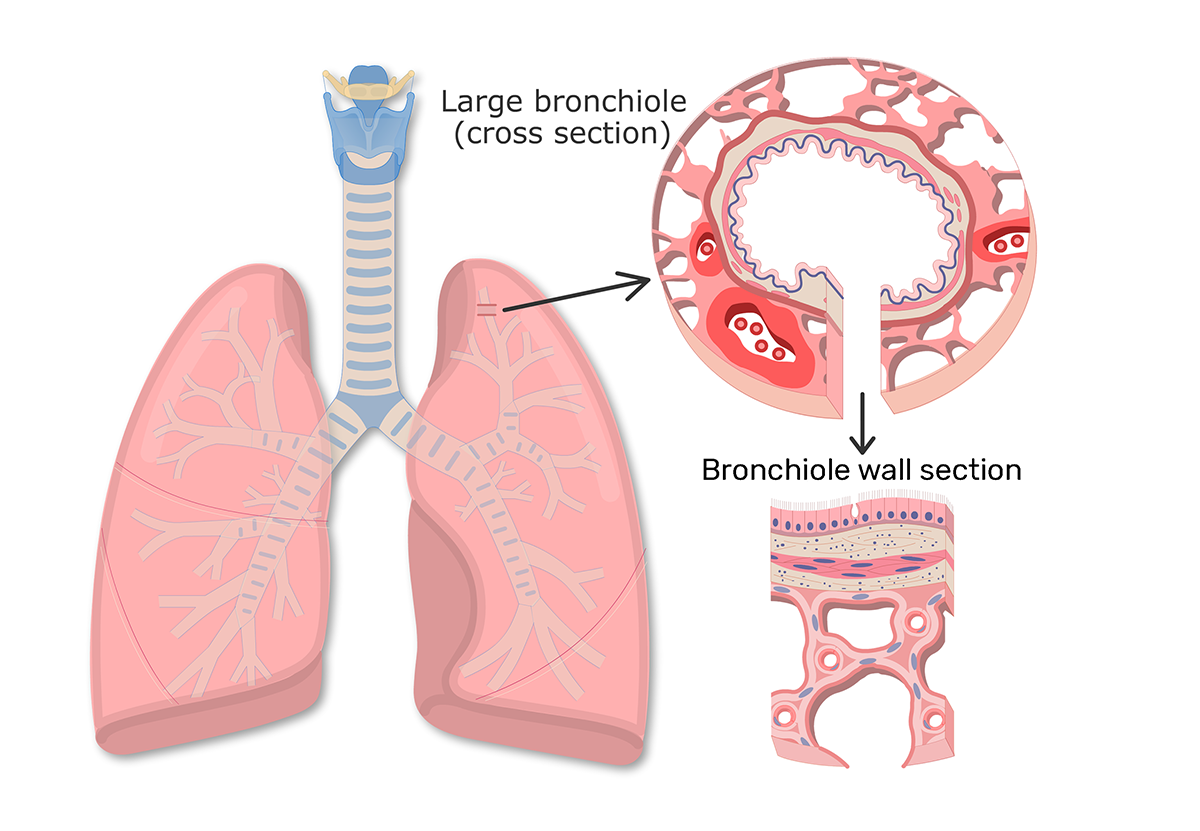
Bronchial wall thickening is an imaging descriptor used to describe abnormal thickening of bronchial walls and can arise from a vast number of pathological entities. It is one of the causes of peribronchial cuffing. The presence of bronchial wall thickening usually (but not always) implies inflammation of the airways..
ON RADIOLOGY Bronchiectasis in HighResolution CT
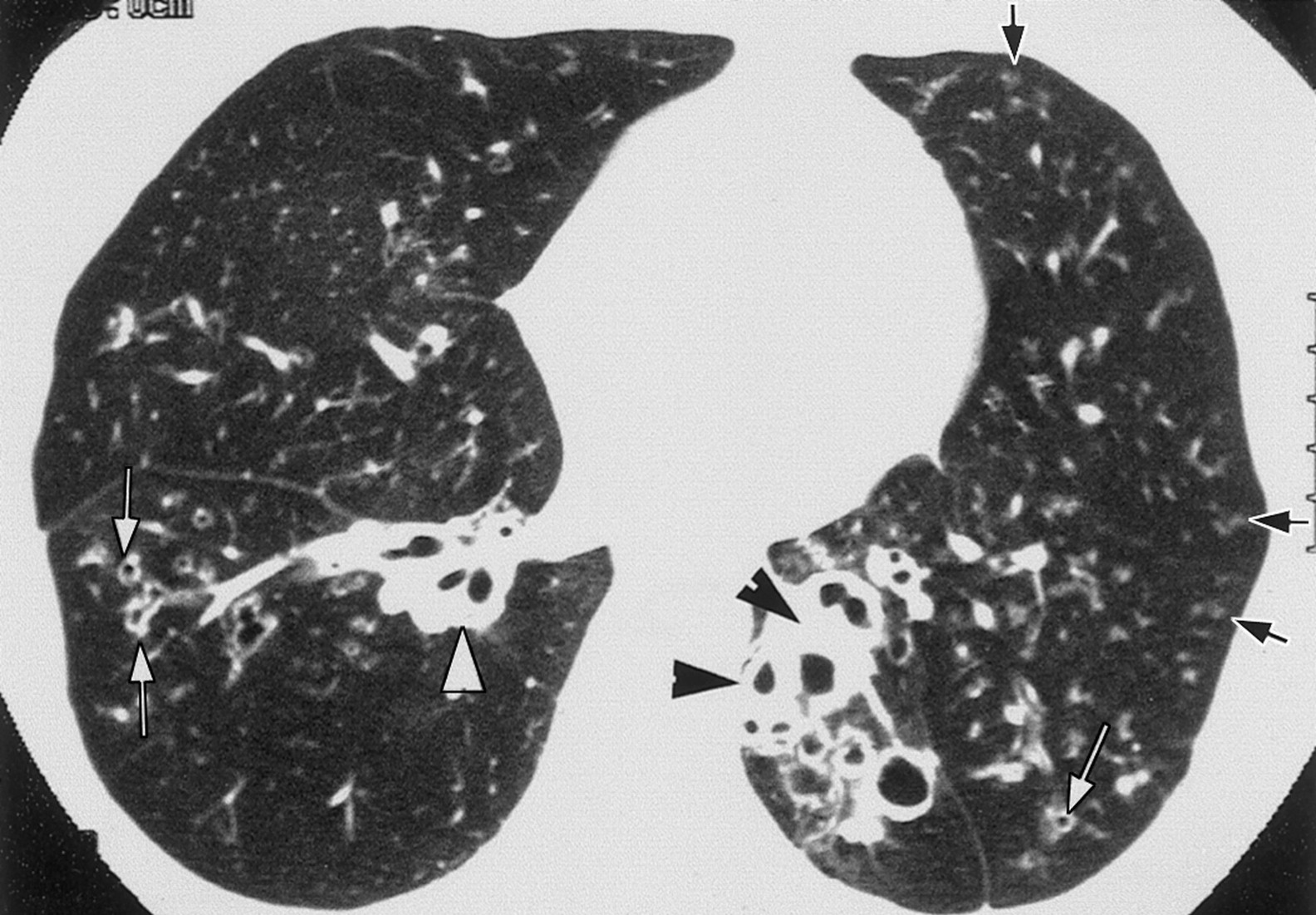
Lymphadenopathy due to mycobacterial infection sometimes causes bronchial obstruction and focal bronchiectasis. As ongoing inflammation changes airway anatomy, pathogenic bacteria (sometimes including mycobacteria), colonize the airways.. X-ray findings suggestive of bronchiectasis involve thickening of the airway walls and/or airway.
Chest CT without contrast revealing (a) bronchial wall thickening and... Download Scientific

Bronchiectasis is a clinical syndrome characterized by cough and sputum production in the presence of abnormal thickening and dilation of the bronchial wall that is visible on lung imaging. 1.
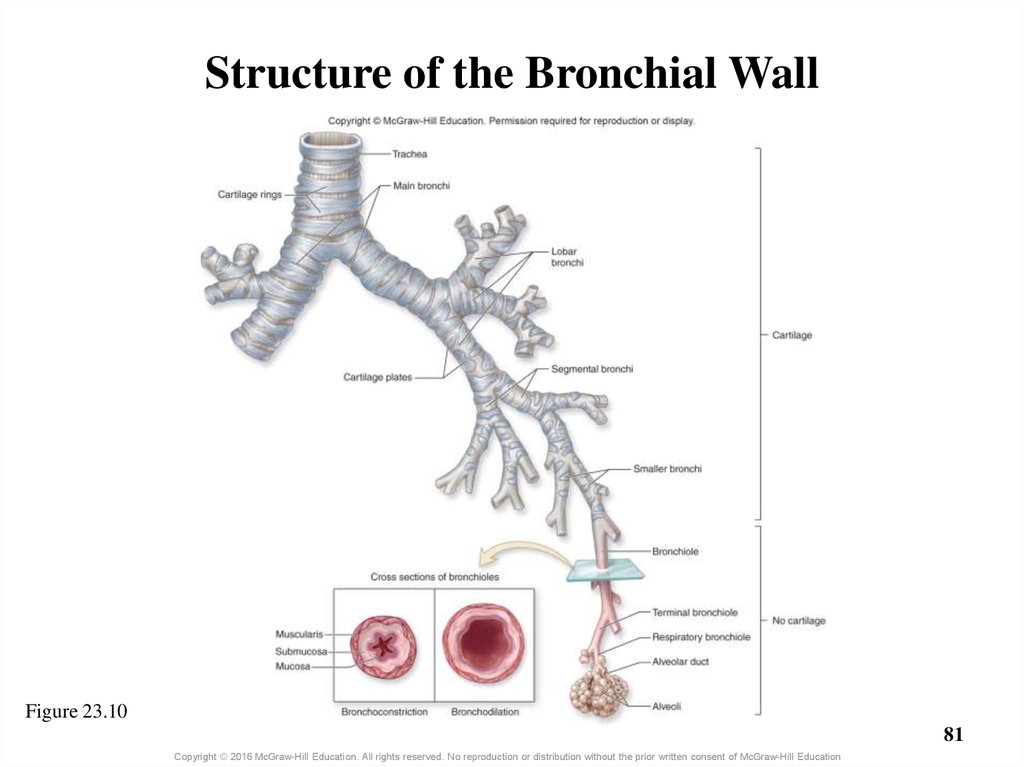
Chapter 23 Part 1 Lecture Outline online presentation
An alternative definition of wall thickening is internal diameter of the airway lumen less than 80% of its external diameter. This definition is useful but only when bronchial dilatation is relatively mild; plainly, if the dilatation is marked (as in cystic bronchiectasis), wall thickening will be underestimated. Mosaic Attenuation.
(PDF) Thickening of the posterior wall of the bronchus intermedius in right lung pneumonia

Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from your lungs. People who have bronchitis often cough up thickened mucus, which can be discolored. Bronchitis may be either acute or chronic. Often developing from a cold or other respiratory infection, acute bronchitis is very common.
Thickening of the bronchial wall in cases of pulmonary emphysema. High... Download Scientific

Given that bronchial wall thickening in the absence of definite lung parenchymal abnormalities is a common feature in eosinophilic asthma , such imaging may be a useful clinical marker for applying anti-eosinophil therapy, including mepolizumab, in EGPA. In our case, we used combination therapy to decrease organ damage and achieve rapid.
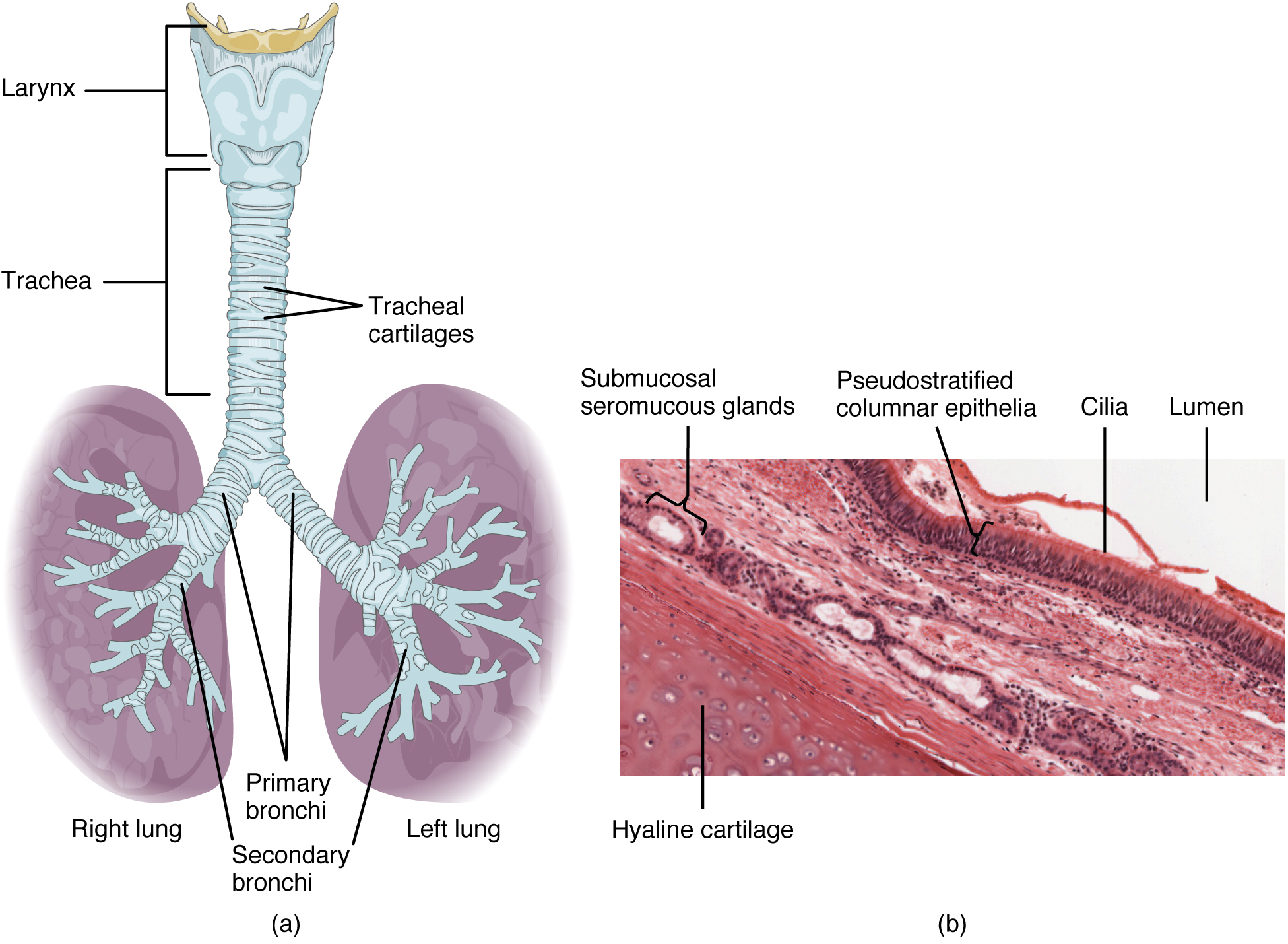
Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Medical Terminology An Interactive Approach
Bronchiectasis. Bronchiectasis is an irreversible widening (dilation) of portions of the breathing tubes or airways (bronchi) resulting from damage to the airway wall. The most common cause is severe or repeated respiratory infections, often in people who have an underlying problem with their lungs or immune system.